 Switching between screens (Activities) is a core concept in Android development. Whether you're building a login flow, a multi-page form, or a simple app with multiple views, you'll need to understand how to navigate from one Activity to another using Intents. In this blog post, we’ll walk you through how to switch activities with just a button click.
Switching between screens (Activities) is a core concept in Android development. Whether you're building a login flow, a multi-page form, or a simple app with multiple views, you'll need to understand how to navigate from one Activity to another using Intents. In this blog post, we’ll walk you through how to switch activities with just a button click.
1. What is an Intent?
In Android, an Intent is a messaging object used to request an action from another component, such as starting a new activity, sending a broadcast, or starting a service.
There are two types of intents:
Explicit Intents: Used to start a specific component (e.g., SecondActivity).
Implicit Intents: Used to invoke components from other apps.
Today, we'll focus on explicit intents.
2. Step-by-Step Implementation
1️. Create Two Activities
Let’s say you have two activities:
MainActivity.java
SecondActivity.java
To create a new activity:
Right-click on the java folder → New → Activity → Empty Activity → Name it SecondActivity.
2️. Design the Layout
activity_main.xml
activity_second.xml
MainActivity.javapackage com.softwaretechit.intentexample;
import android.content.Intent;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.View;import android.widget.Button;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btnSwitch;
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btnSwitch = findViewById(R.id.btnSwitch);
btnSwitch.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // Create an Intent to start SecondActivity Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); }}
✅ Don’t Forget to Update AndroidManifest.xml
You must declare every activity in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<application
... >
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity" />
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
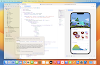
🎉 Result
When you run the app and click the "Go to Second Activity" button, it will open the SecondActivity screen. Just like that — you’ve successfully switched activities using intents!
🧠 Final Thoughts
Using intents to switch between activities is a fundamental skill in Android development. Once you get comfortable with this pattern, you can expand your app’s functionality by passing data between activities using putExtra() and retrieving it with getIntent().
📌 Follow SoftwareTechIT for more beginner-friendly Android tutorials!
If you have any questions or want a deeper dive into passing data between activities or using implicit intents, let us know in the comments below. Happy coding!


















0 Comments